Edvancer's Knowledge Hub
How to shift your career to Analytics like a boss

Analytics.
You’re obsessed with the field, with each blog, book and article you come across.
But you’re afraid.
You’re afraid of the number of different jobs within analytics. You’re afraid that your current experience might not be considered when you switch to analytics from your current career. You’re afraid of not having a background in analytics or programming.
Well, I doubt you can make a successful career change until you have a game plan for the transition. My goal is to give you this game plan.
How is analytics different from big data and business intelligence?
Many people confuse analytics with big data and business intelligence. Let’s first put this confusion to rest.
Business intelligence is the process of using software and tools to collate, process and analyze structured data, and visualize this data using dashboards. Using these facts and figures can a business manager take informed decisions. WHAT is happening to a business = Business Intelligence.
Analytics is about investigation—why something is happening, and what will most likely happen in the future.
The data we use in business intelligence and analytics is structured and not of huge volume, variety or velocity.
If the data significant to your business is of very high volume, variety & velocity then you need different set of software/hardware capabilities to process this data and get meaningful insights out of it. Data of
this nature is called Big Data and the associated tools & technologies are called Big Data technologies.
In this article, we are going to discuss only jobs related to analytics.
Different jobs within analytics:
Business analyst:
A business analyst is an expert in the industry in which he operates, be it finance, manufacturing, retail or research.
Business analysts are also good at data manipulation and often analyze using spread sheets and data base tools.
In startups and small companies, business analysts are also expected to know the basics in SQL, R and statistics. However, their core competency lies in communicating the results/conclusions derived from the data to the end stakeholders – it can be the customer, senior management, or investors.
Most jobs like marketing analyst, digital analyst and financial analyst also fall under the category of a business analyst.
Check out this post to understand what it takes to become a business analyst: 6 steps to becoming a business analytics professional
 Predictive analytics
Predictive analysts are the in-betweeners of data science and data analysis. They are also called junior data scientists.
They are good at one predictive analytics tool (like R, SAS, Python or Stata), SQL, have a basic understanding of statistics and have a good knowledge of how predictive techniques like regression and clustering are applied to a particular domain.
How to choose the right job role for you
By now, you have a fair idea of what responsibilities are involved in each role. If you have a business background and an experience in streams like product management, project management, client delivery, or business consulting, then it is easier to transition into the job of a business analyst. Whereas, if you come from a business intelligence, data base or engineering back ground, i.e those with experience in data architecture, information management, server or system administration, then it is easier to become a data analyst.
Conclusion
Knowledge in a particular domain is one of the most overlooked factors when you are attempting to change your career. If, for instance, you are looking to become a data analyst in the marketing industry, then you need to understand the terminologies and jargons like customer churn, marketing funnel, bounce rate, conversion ratio used in this industry. Take advantage of your domain knowledge when you are trying to switch careers.
Let me give one more example. If you have 5 years’ experience working as a database admin, your ideal analytics job category would be a Data Analyst.
If you lack the necessary skills for a particular job, then you can take online courses to fill the gap. Online courses will teach you how to solve real-world analytics problems right from scratch, so that you gain the hands-on experience that companies are looking for, and you also have a robust portfolio of projects to demonstrate your capabilities. Make sure these courses are taught by industry professionals who have extensive experience in the analytics industry, so that they have the ability to review your resume and mentor you to successfully transition your career to analytics.
Hope I have given you a clear plan on how to transition your career to analytics. Drop in a comment if you have any further questions!
Predictive analytics
Predictive analysts are the in-betweeners of data science and data analysis. They are also called junior data scientists.
They are good at one predictive analytics tool (like R, SAS, Python or Stata), SQL, have a basic understanding of statistics and have a good knowledge of how predictive techniques like regression and clustering are applied to a particular domain.
How to choose the right job role for you
By now, you have a fair idea of what responsibilities are involved in each role. If you have a business background and an experience in streams like product management, project management, client delivery, or business consulting, then it is easier to transition into the job of a business analyst. Whereas, if you come from a business intelligence, data base or engineering back ground, i.e those with experience in data architecture, information management, server or system administration, then it is easier to become a data analyst.
Conclusion
Knowledge in a particular domain is one of the most overlooked factors when you are attempting to change your career. If, for instance, you are looking to become a data analyst in the marketing industry, then you need to understand the terminologies and jargons like customer churn, marketing funnel, bounce rate, conversion ratio used in this industry. Take advantage of your domain knowledge when you are trying to switch careers.
Let me give one more example. If you have 5 years’ experience working as a database admin, your ideal analytics job category would be a Data Analyst.
If you lack the necessary skills for a particular job, then you can take online courses to fill the gap. Online courses will teach you how to solve real-world analytics problems right from scratch, so that you gain the hands-on experience that companies are looking for, and you also have a robust portfolio of projects to demonstrate your capabilities. Make sure these courses are taught by industry professionals who have extensive experience in the analytics industry, so that they have the ability to review your resume and mentor you to successfully transition your career to analytics.
Hope I have given you a clear plan on how to transition your career to analytics. Drop in a comment if you have any further questions!
Share this on





Follow us on




Learn Business Analytics from Edvancer.
Data analyst The main task of a data analyst is to collect, manipulate and analyze data. He prepares reports, which may be in the form of visualizations such as graphs, charts or dashboards, detailing the significant results they deduced. Data analysts have a strong knowledge in relational databases like SQL, and know how to retrieve and store data in these databases. They often have a thorough understanding of relationships that exist between the organization’s various databases. Data analysts who also know technologies like Hive, Pig and how to set up a brand operate a Hadoop ecosystem command a higher salary. Data scientist “A data scientist is half hacker, half analyst, and he uses data to build and derive insights” – Monica Rogati A data scientist is well versed with R, SQL, advanced statistics, machine learning and has a respectable amount of knowledge in a particular industry (like banking, hospitality, etc.) Drew Conway created the Venn diagram to define a data scientist: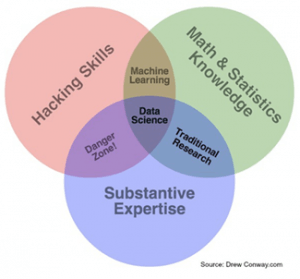 Predictive analytics
Predictive analysts are the in-betweeners of data science and data analysis. They are also called junior data scientists.
They are good at one predictive analytics tool (like R, SAS, Python or Stata), SQL, have a basic understanding of statistics and have a good knowledge of how predictive techniques like regression and clustering are applied to a particular domain.
How to choose the right job role for you
By now, you have a fair idea of what responsibilities are involved in each role. If you have a business background and an experience in streams like product management, project management, client delivery, or business consulting, then it is easier to transition into the job of a business analyst. Whereas, if you come from a business intelligence, data base or engineering back ground, i.e those with experience in data architecture, information management, server or system administration, then it is easier to become a data analyst.
Conclusion
Knowledge in a particular domain is one of the most overlooked factors when you are attempting to change your career. If, for instance, you are looking to become a data analyst in the marketing industry, then you need to understand the terminologies and jargons like customer churn, marketing funnel, bounce rate, conversion ratio used in this industry. Take advantage of your domain knowledge when you are trying to switch careers.
Let me give one more example. If you have 5 years’ experience working as a database admin, your ideal analytics job category would be a Data Analyst.
If you lack the necessary skills for a particular job, then you can take online courses to fill the gap. Online courses will teach you how to solve real-world analytics problems right from scratch, so that you gain the hands-on experience that companies are looking for, and you also have a robust portfolio of projects to demonstrate your capabilities. Make sure these courses are taught by industry professionals who have extensive experience in the analytics industry, so that they have the ability to review your resume and mentor you to successfully transition your career to analytics.
Hope I have given you a clear plan on how to transition your career to analytics. Drop in a comment if you have any further questions!
Predictive analytics
Predictive analysts are the in-betweeners of data science and data analysis. They are also called junior data scientists.
They are good at one predictive analytics tool (like R, SAS, Python or Stata), SQL, have a basic understanding of statistics and have a good knowledge of how predictive techniques like regression and clustering are applied to a particular domain.
How to choose the right job role for you
By now, you have a fair idea of what responsibilities are involved in each role. If you have a business background and an experience in streams like product management, project management, client delivery, or business consulting, then it is easier to transition into the job of a business analyst. Whereas, if you come from a business intelligence, data base or engineering back ground, i.e those with experience in data architecture, information management, server or system administration, then it is easier to become a data analyst.
Conclusion
Knowledge in a particular domain is one of the most overlooked factors when you are attempting to change your career. If, for instance, you are looking to become a data analyst in the marketing industry, then you need to understand the terminologies and jargons like customer churn, marketing funnel, bounce rate, conversion ratio used in this industry. Take advantage of your domain knowledge when you are trying to switch careers.
Let me give one more example. If you have 5 years’ experience working as a database admin, your ideal analytics job category would be a Data Analyst.
If you lack the necessary skills for a particular job, then you can take online courses to fill the gap. Online courses will teach you how to solve real-world analytics problems right from scratch, so that you gain the hands-on experience that companies are looking for, and you also have a robust portfolio of projects to demonstrate your capabilities. Make sure these courses are taught by industry professionals who have extensive experience in the analytics industry, so that they have the ability to review your resume and mentor you to successfully transition your career to analytics.
Hope I have given you a clear plan on how to transition your career to analytics. Drop in a comment if you have any further questions!
Manu Jeevan
Manu Jeevan is a self-taught data scientist and loves to explain data science concepts in simple terms. You can connect with him on LinkedIn, or email him at manu@bigdataexaminer.com.
Latest posts by Manu Jeevan (see all)
- Python IDEs for Data Science: Top 5 - January 19, 2019
- The 5 exciting machine learning, data science and big data trends for 2019 - January 19, 2019
- A/B Testing Made Simple – Part 2 - October 30, 2018
Follow us on
Free Data Science & AI Starter Course

